Speed vs. Precision: Optimizing Your Packaging Line with the Right Wrapping Machine
Speed vs. Precision: Optimizing Your Packaging Line with the Right Wrapping Machine
In modern manufacturing and logistics, packaging performance directly affects throughput, cost control, and shipment safety. The real challenge is not choosing speed or precision—but selecting the right Packaging Line Wrapping Machine that balances both for your specific operation. At Innovative WrapTech Pvt. Ltd., packaging engineers see firsthand how incorrect machine selection leads to film waste, unstable loads, bottlenecks, and unnecessary downtime.
This guide explains how wrapping machines work, why they are critical to industrial operations, and how to optimize your packaging line by aligning machine speed, wrapping accuracy, and automation level.
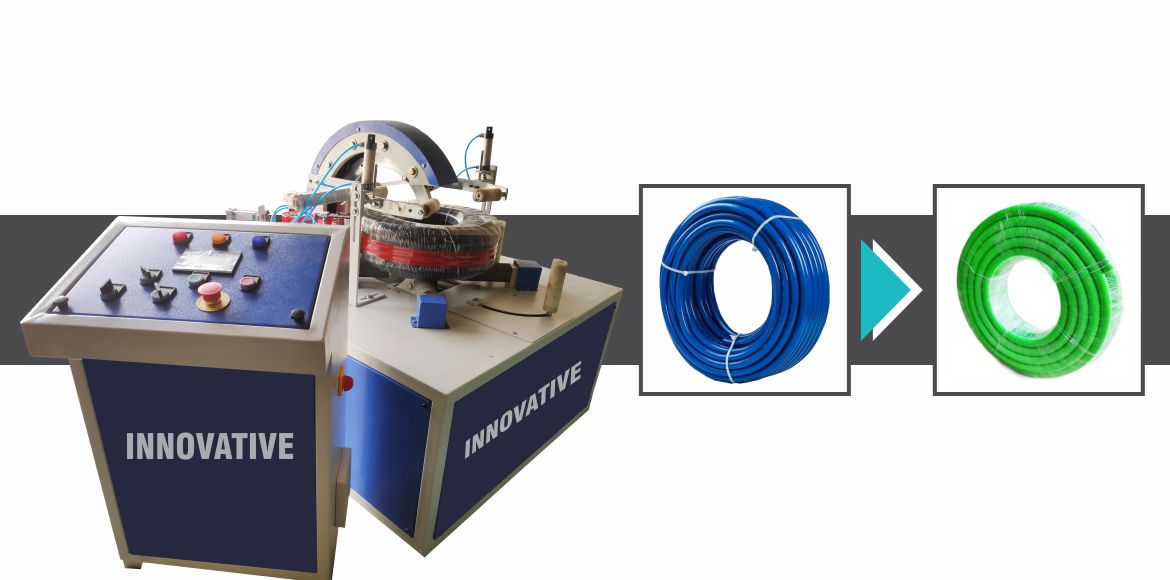
What Is an Industrial Wrapping Machine?
An industrial wrapping machine applies stretch film or protective wrap around palletized or packaged goods to stabilize loads during storage and transportation. Unlike manual wrapping, machines deliver consistent tension, repeatable wrap patterns, and controlled film usage.
From a production standpoint, wrapping machines serve three core functions:
Load containment
Product protection
Packaging line efficiency
Choosing the wrong machine compromises one or more of these outcomes.
Step-by-Step: How a Packaging Line Wrapping Machine
A standard automated or semi-automatic pallet wrapping process follows these stages:
Pallet Positioning
The operator or conveyor places the pallet on a turntable or stationary platform.Film Attachment
The film tail attaches manually or automatically to the pallet base.Film Pre-Stretch Control
Powered rollers stretch the film (typically 200–300%) to maximize strength and reduce consumption.Wrap Cycle Execution
Turntable rotation or rotating arm movement
Vertical carriage travel applies programmed wrap patterns
Variable tension adjusts for load stability
Top & Bottom Reinforcement
Extra wraps secure load bases and tops for transport safety.Film Cut & Seal
Automatic systems cut and clamp the film for the next cycle.
Each step affects speed, load integrity, and film cost.
Why Wrapping Machines Are Critical in Modern Industrial Operations
Manufacturers rely on wrapping machines because they:
Increase packaging line speed without sacrificing consistency
Reduce stretch film usage by 30–40%
Improve pallet stability and reduce transit damage
Standardize packaging quality across shifts
Lower labor dependency and operator fatigue
For high-volume facilities, Packaging Line Wrapping Machine are no longer optional—they are production-critical assets.
Speed vs. Precision: Understanding the Trade-Off
| Factor | High-Speed Focus | High-Precision Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Output | Maximum pallets/hour | Optimized load stability |
| Film Use | Higher if uncontrolled | Lower with pre-stretch |
| Best For | FMCG, logistics hubs | Pharma, chemicals, exports |
| Risk | Load shift if unchecked | Slightly lower throughput |
The right solution balances both—speed where volume demands it, precision where product risk requires it.
Types of Wrapping Machines and When to Use Them
1. Semi-Automatic Turntable Wrappers
Best for: Small to medium operations
Advantages:
Cost-effective
Easy to operate
Adjustable wrap programs
2. Fully Automatic Inline Wrappers
Best for: High-throughput production lines
Advantages:
Conveyor integration
Automatic film handling
Consistent cycle times
3. Rotary Arm Wrapping Machines
Best for: Heavy, unstable, or tall loads
Advantages:
No pallet rotation
Ideal for fragile goods
4. Ring-Type High-Speed Wrappers
Best for: Distribution centers
Advantages:
Extremely fast cycle times
Designed for uniform pallet loads
Installation Best Practices
To achieve optimal performance:
Ensure level flooring and vibration-free foundations
Maintain correct power supply and grounding
Align conveyors precisely for automatic systems
Train operators before production launch
Incorrect installation reduces machine lifespan and wrapping accuracy.
Operation & Maintenance Best Practices
Daily
Inspect film carriage and rollers
Check sensors and safety guards
Clean dust from moving components
Weekly
Lubricate mechanical parts
Inspect belts, chains, and drives
Review wrap program settings
Long-Term
Replace worn rollers and bearings
Update PLC software if applicable
Conduct load containment audits
Preventive maintenance preserves speed consistency and wrap precision.
Why Manufacturers Prefer Professional-Grade Machines
From factory-floor experience, professional machines:
Deliver consistent performance across shifts
Handle production scaling without upgrades
Protect brand reputation through stable packaging
Cheap alternatives increase hidden costs through downtime, film waste, and rejected shipments.
Future Trends and Smart Factory Integration
Wrapping machines are evolving into data-driven assets:
IoT-enabled performance tracking
ERP and WMS integration
Predictive maintenance alerts
Automated wrap optimization
Energy usage monitoring
Smart factories treat wrapping machines as intelligent nodes, not standalone equipment.
FAQs (Buyer-Focused)
Q1. How do I choose between speed and precision in a wrapping machine?
You should base the decision on product stability, pallet weight, and throughput needs. High-volume operations prioritize speed, while fragile or export goods require higher wrapping precision.
Q2. What type of wrapping machine is best for high-speed packaging lines?
Fully automatic inline and ring-type wrapping machines work best for high-speed packaging lines due to their fast cycle times and conveyor integration.
Q3. Which wrapping machine offers the highest precision for unstable loads?
Rotary arm and semi-automatic pallet wrapping machines offer higher precision because they provide controlled film tension and customizable wrap patterns.
Q4. How does a professional Packaging Line Wrapping Machine improve ROI?
Professional-grade machines reduce film consumption, lower labor costs, minimize product damage, and ensure consistent uptime, resulting in ROI within 6–18 months.
Q5. Why should manufacturers avoid low-cost wrapping machines?
Low-cost machines often lack safety features, consistent pre-stretch control, and long-term reliability, leading to higher maintenance costs and operational risks.